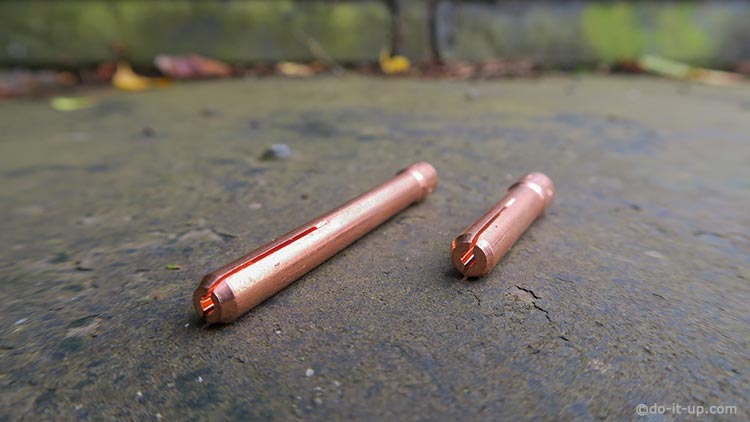
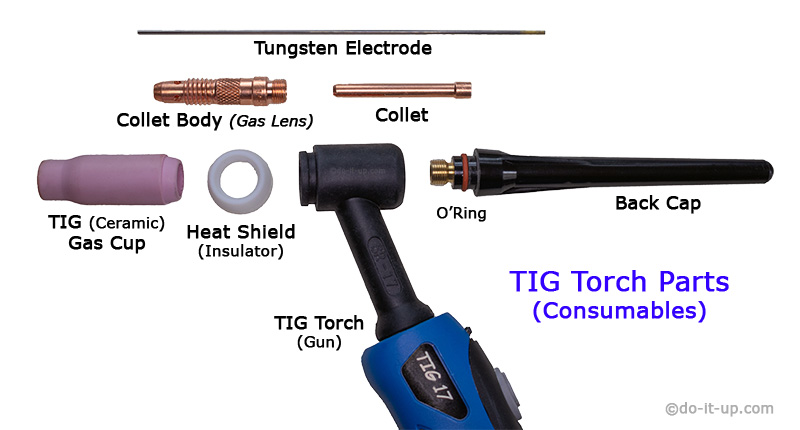
TIG Collets:
A collet holds the Tungsten electrode. When you screw on the back cap, it pushes the collet against the gas nozzle, which squeezes the collet jaws. This makes a good electrical contact, holds the Tungsten electrode in place and prevents the Tungsten electrode from moving. To adjust the Tungsten electrode, you loosen the back cap, move the Tungsten electrode. when adjustment is complete, re-tighten the back cap.

Topics:
TIG Collet Types:
TIG Collet Types – Names Used:
| Consumable | Names Used |
|---|---|
| Collet | Standard |
| Stubby | |
| Wedge | |
| Reverse |
Types:
Standard (Long):
The ‘Standard’ collet is the longer collet that fits a bog stand gas lens.
Stubby:
A ‘Stubby’ collet is a shorter collet that fits the shorter stubby gas lens, or the wide gas lens (that often have a diffuser fitted).
Wedge:
A ‘Wedge’ collet has an angled end and no slots down the side of the collet. A fault with ‘slotted’ collets is that they can become twisted and deformed if overtightened. The wedge collet overcomes this issue.
How do they work? – The offset chamfer forces the collet to one side when screwing in the back cap, thereby wedging the Tungsten electrode in place. The Tungsten electrode may need a little push to get it to release when removing. Because there are no slots in a ‘Wedge’ collet, they last longer.
- They prevent twisting and deformation when tightening.
- Provide better electrical contact, less resistance and heat.
- Last longer than ‘slotted’ collets.
Reverse:
A ‘Reverse’ collet is much shorter, with the clamping slots on the opposite end.
How do they work? – They are wider than the other collets, so they sit on the back of the gas lens, rather than sliding all the way inside the gas lens body. They are slotted on the opposite end, so that the back cap squeezes the slots clamping the Tungsten electrode, (rather than the back cap pushing the collet into the gas lens).
Notes:
- Available with a variety of size holes to fit the different size Tungsten electrodes.
- Make sure they fit your type of TIG torch before purchasing.
How do TIG Collets Work?
The TIG collet is placed inside the head of the TIG torch, (against the gas nozzle). The Tungsten electrode slides into the collet and through the gas nozzle. The back cap is then screwed into the back of the torch head.
Topics:
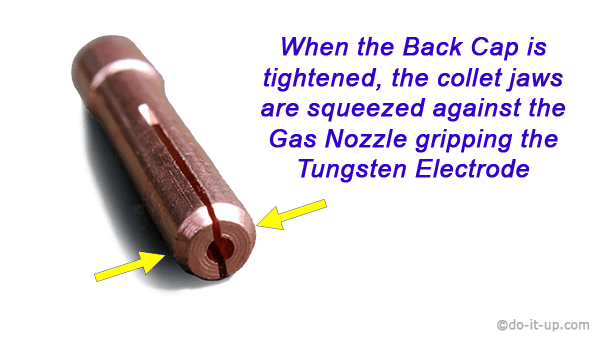
Tightening a TIG Collet:
When the back cap is tightened, the jaws of the collet are squeezed against the gas nozzle, gripping the tungsten electrode.
Adjusting a TIG Collet (Tungsten Electrode):
Loosen the TIG torch back cap and move the Tungsten electrode to the position required. Retighten the back cap.
Notes:
- Make sure the TIG torch has cooled before adjusting.
- Sometimes the Tungsten electrode can stick, so a little ‘jiggling’ may be needed.
- Wedge collets work in a slightly different manner – An offset chamfer forces the collet to one side when screwing in the back cap.
TIG Collet Sizes:
Tig collet sizes are defined by the size of the Tungsten electrodes they hold, (see the article on different size Tungsten electrodes, typically between 1.0mm (0.040″) and 6.35mm (1/4″)).
As you can see, the outside diameter tends to remain the same for a set of collets, however the length can vary and are often classified as standard (long), or stubby. The actual length may vary between manufacturers.

Note:
The nozzles will need to fit the size of TIG torch being used. This is often split into two groups – See the article Which Parts Fit Which TIG Torch?
Image Gallery:
– click or tap the image to view full size –
